Product Introduction
Types of Automatic Laser Welding Machines
-
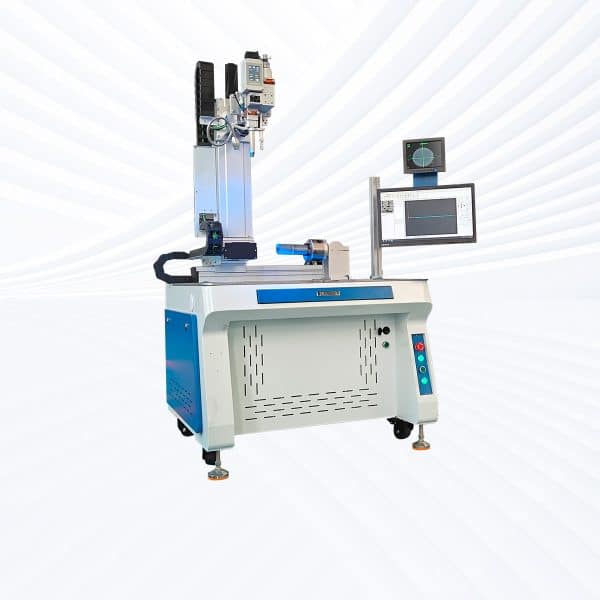

Automatic Laser Welding Platform
Rated 4.75 out of 5$9,800.00 – $21,500.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Automatic Laser Welding Robot
Rated 4.75 out of 5$13,800.00 – $25,500.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Application of Automatic Laser Welding Machines







Customer Testimonials
Automatic Laser Welding Machine VS Other Welding Machines
| Comparison Item | Automatic Laser Welding Machine | TIG Welding Machine | MIG Welding Machine | Stick Welding Machine | Plasma Arc Welding Machine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automation Capability | Fully automated, programmable | Limited | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
| Welding Speed | Very high | Slow | Fast | Medium | Fast |
| Precision | Extremely high | High | Medium | Low | Medium |
| Consistency | Excellent, repeatable results | Operator-dependent | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
| Heat Input | Low (minimal distortion) | Low | Medium | High | High |
| Joint Quality | High strength, clean finish | High | High | Medium | High |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, minimal post-processing | Smooth | Acceptable | Rough | Rough |
| Labor Requirement | Minimal | High | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Operating Cost | Low long-term | High (due to slow speed) | Moderate | Low | High |
| Consumables Usage | Very low | Electrodes + gas | Wire + gas | Electrodes | Electrodes + gas |
| Waste and Spatter | Very low | Low | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Integration with Robotics | Excellent | Difficult | Moderate | Not suitable | Moderate |
| Material Compatibility | Wide (metals including aluminum) | Best for thin metals | Steel, aluminum | Mostly steel | Conductive metals |
| Application Scope | Mass production, complex welding | Small-scale, precision work | Structural, general fabrication | Repairs, outdoor work | Cutting + joining tasks |
| Productivity | High throughput | Low | Moderate to high | Medium | Moderate |
Why Choose Us
High Precision
Our machines deliver accurate, clean welds with minimal heat input, reducing distortion and ensuring strong, consistent joints across a wide range of materials and thicknesses.
Easy Operation
Designed with intuitive controls and user-friendly interfaces, our systems allow both experienced operators and new users to achieve professional results with minimal training.
Durable & Reliable
Built with high-quality components and strict quality standards, our welding machines provide stable performance, long service life, and low maintenance requirements.
Custom Options
We offer a variety of models and customizable features to match specific production needs, helping businesses improve workflow and adapt to changing manufacturing demands.
Related Resources
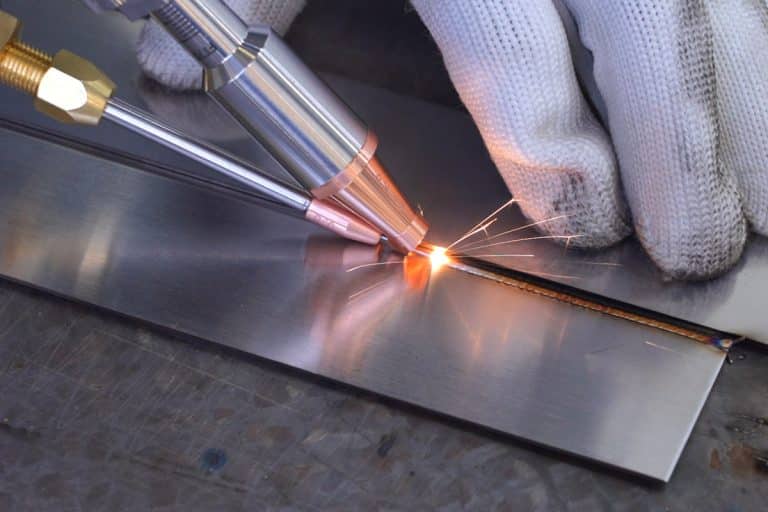

What Is Laser Welding?
Explore the principles of laser welding, its benefits, applications, and how it compares to traditional welding methods. Learn how this advanced technology enhances precision and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
What Power Options Are Available For Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- 1500W: Suitable for thin materials and precision welding tasks. Ideal for small components in electronics, medical devices, or fine metalwork.
- 2000W: A balanced choice for medium-thickness metals, offering good welding speed and penetration for applications like automotive parts and structural components.
- 3000W: Designed for higher productivity and thicker materials. Commonly used in heavy-duty manufacturing, including steel structures and machinery.
- 6000W: High-power output for deep welds, thick metal plates, and high-speed, high-volume industrial applications such as shipbuilding or heavy equipment.
What Materials Can Be Welded With Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- Carbon Steel: Widely used in construction and manufacturing, carbon steel welds cleanly and efficiently with laser welding systems.
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for laser welding due to its high strength and corrosion resistance. Common in automotive, medical, and food processing applications.
- Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys: Requires higher power due to high reflectivity and thermal conductivity. Automatic laser welding machines can handle aluminum effectively, especially with proper beam control and gas shielding.
- Copper and Copper Alloys: Challenging to weld due to reflectivity, but high-powered laser systems can achieve quality welds. Often used in electronics, batteries, and EV components.
- Titanium: Suitable for high-precision laser welding in aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors. Requires shielding to prevent contamination.
- Nickel Alloys: Laser welding is effective for high-performance nickel alloys used in aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing.
- Brass: Can be laser welded for electrical and decorative applications, though care must be taken due to its zinc content.
What Types Of Joints Are Suitable For Automatic Laser Welding?
- Butt Joints: Two pieces are placed edge to edge. Ideal for welding sheets and plates of the same thickness. Common in automotive and structural applications.
- Lap Joints: One material overlaps the other. Well-suited for thin metals, battery tabs, or sheet metal work. Often used when part alignment is easier in an overlapping setup.
- T-Joints: One part is joined at a 90-degree angle to another, forming a T-shape. Common in structural and frame welding where precise fusion at the base is required.
- Corner Joints: Edges of two parts meet at a right angle, forming a corner. Suitable for box or enclosure fabrication where appearance and strength are both important.
- Edge Joints: Used for welding the edges of two sheets that lie in the same plane. Typically used in lightweight or low-stress applications.
- Seam Welds (Continuous Joints): Long, continuous welds along a joint line. Ideal for sealing applications like pipes, enclosures, or containers.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- High Initial Cost: These machines are expensive to purchase and set up. The cost includes not just the laser source, but also automation systems, robotic arms, sensors, and safety enclosures.
- Complex Installation and Setup: Installing and calibrating an automatic laser welding system requires time, expertise, and a controlled environment. It’s not plug-and-play; specialized knowledge is needed for integration into production lines.
- Limited Flexibility for Custom or One-Off Jobs: Automatic systems are designed for repetitive, high-volume tasks. They’re less efficient or cost-effective for small batch or custom welding jobs where frequent setup changes are needed.
- Sensitivity to Joint Fit-Up and Tolerances: Laser welding requires precise joint alignment and minimal gaps. Any variation in part fit-up can result in poor-quality welds or defects, meaning pre-weld part preparation must be exact.
- Maintenance and Downtime: These systems have multiple components (optics, robotics, cooling, software), which require regular maintenance. If something fails, downtime can be costly and repairs complex.
- Operator Training Required: Despite being automated, trained personnel are still needed to program, monitor, and maintain the system. Improper use can lead to subpar welds or equipment damage.
- Not Ideal for All Materials or Thicknesses: Highly reflective or very thick materials may require more power, different laser types, or may be better suited to other welding methods depending on the application.
What Are The Hazards Of Automatic Laser Welding?
- Eye Injuries: Laser beams—especially high-powered ones—can cause permanent eye damage from direct or reflected exposure. Even brief contact with the beam can burn the retina.
- Skin Burns: The intense laser energy can cause serious skin burns on contact. While automated systems still require occasional manual intervention, increasing the risk if safety protocols aren’t followed.
- Fire Hazards: Laser beams can ignite flammable materials, especially in areas with dust, oil, or vapors. Automatic machines operating continuously increase the risk if the environment isn’t controlled.
- Harmful Fumes and Gases: Laser welding can produce toxic fumes, metal vapors, and particulates, especially when welding coated or treated metals. Without proper fume extraction, these can pose serious respiratory risks.
- Electrical Hazards: Automatic laser welding machines run on high-voltage components, including laser generators, motors, and control systems. Faulty wiring, improper grounding, or poor maintenance can lead to shocks or equipment failure.
- Mechanical Hazards: Moving parts such as robotic arms or automated stages can cause pinching, crushing, or collision injuries if safety zones are breached or sensors fail.
- Noise Exposure: Some high-powered systems generate loud operational noise, especially when integrated into large production lines. Prolonged exposure may require hearing protection.
- Software and Control Failures: Programming errors or sensor malfunctions can cause unintended motion, incorrect weld paths, or unsafe operation, risking both the machine and operator safety.
What Is The Lifespan Of Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- Laser Source Quality: High-quality fiber lasers from reputable brands (like IPG, Raycus, Max) can last up to 100,000 hours or more.
- Usage Intensity: Machines used in continuous, high-volume production may wear faster than those used intermittently.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning, filter changes, alignment checks, and component replacement can significantly extend service life.
- Environment: Clean, dust-free, and temperature-controlled environments reduce stress on sensitive components and electronics.
- Component Wear: While the laser source may last for years, parts like lenses, nozzles, motors, and cooling units may need periodic replacement.
How Do I Maintain Automatic Laser Welding Machines?
- Clean Optical Components
- Regularly inspect and clean the laser lens, mirrors, and protective windows using proper lens wipes and solvents.
- Dirty or damaged optics can reduce beam quality and cause power loss or beam distortion.
- Maintain the Cooling System
- Check coolant levels (for water-cooled systems) and inspect hoses, filters, and pumps.
- Clean dust and debris from fans or air vents in air-cooled systems to prevent overheating.
- Inspect Mechanical Parts
- Lubricate moving components like guide rails, robotic arms, and actuators as recommended.
- Check for wear, alignment issues, or loose fasteners that may affect precision.
- Replace Consumables
- Replace nozzles, protective covers, gas lenses, and filters at regular intervals.
- Monitor gas lines and shielding gas supplies for leaks or blockages.
- Electrical and Safety Checks
- Inspect cables, connectors, and circuit boards for wear or corrosion.
- Test emergency stop buttons, interlocks, and light curtains to ensure all safety systems are working correctly.
- Run System Diagnostics
- Use built-in software tools to check for laser output stability, beam alignment, and machine health.
- Record and track machine performance for preventive maintenance planning.
- Keep the Work Area Clean
- Remove metal dust, debris, and spatter from the machine and surroundings.
- A clean environment helps protect optics, electronics, and mechanical systems from contamination.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Maintenance Schedule
- Stick to the maintenance intervals specified in the user manual for tasks like filter changes, recalibration, and servicing.
