How to prevent the hazards caused by laser welding?
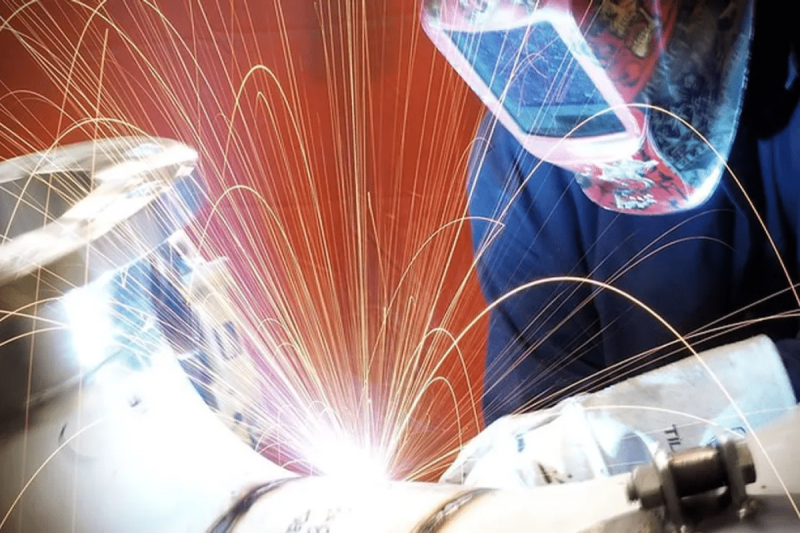

How laser welding works
Laser welding is a highly precise welding technology that uses a laser beam to locally heat the workpiece, causing it to instantly melt and realize the welding process. Its working principle involves multiple links such as laser generation, focusing, irradiation, and heat transfer. The specific working principle is as follows:
- Laser generation and amplification: After the active medium is excited, the laser generator generates a laser beam. This laser beam is amplified and focused through optical elements, such as mirrors and lenses so that the laser beam can be accurately focused on small points during the welding process.
- Beam focusing and high energy density: Through optical components such as lenses, the laser beam is focused into a tiny and high-energy focus, which enables the laser to provide a large amount of heat in a very short time and achieve high energy density.
- Material melting and welding: The high energy density of the laser beam is concentrated on the surface of the workpiece, causing local areas of the workpiece to instantly heat up and melt. This instantaneous high temperature can cause the material to reach its melting point and form a molten pool. At the moment when the laser beam passes, the molten pool rapidly cools and solidifies, forming a welded joint.
- Precision control and automation: The high energy density of the laser beam is concentrated on the surface of the workpiece, causing local areas of the workpiece to instantly heat up and melt. This instantaneous high temperature can cause the material to reach its melting point and form a molten pool. At the moment when the laser beam passes, the molten pool rapidly cools and solidifies, forming a welded joint.

What are the hazards of laser welding?
Compared with traditional welding methods, laser welding has the advantages of high energy density, precise control, fast operation, and reduction of heat-affected zone. However, there are still a series of potential hazards during its use. The following are the main hazards that may be caused by laser welding:
Light radiation hazards
The intense laser beam produced by laser welding may be harmful to human eyes. The laser beam has high energy and high concentration. If it is directly irradiated into the eyes, it may cause retinal burns, which will affect vision and even cause permanent blindness. In addition to visible light, laser beams may also contain invisible ultraviolet and infrared rays, whose radiation is also potentially harmful to the eyes and skin.
Smoke hazards
During the laser welding process, the fumes generated by the welding materials may contain harmful substances. These harmful substances include, but are not limited to, metal particles, organic substances, and other volatile compounds. Workers exposed to these fumes for a long time can easily cause respiratory problems, such as coughing, shortness of breath, and even chronic respiratory diseases.
gas hazard
Some components in laser welding materials may release toxic gases at high temperatures. For example, toxic gases such as nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide may be harmful to workers’ health. Prolonged exposure to these gases may cause poisoning, manifesting as headache, dizziness, fatigue, and other symptoms.
Noise hazard
Laser welding equipment is usually accompanied by high-intensity noise when working. Prolonged exposure to such high-noise environments can lead to hearing loss and even deafness. Noise not only harms the physical health of workers but may also cause reduced work efficiency and discomfort in the working environment.
Radiation risk
The electromagnetic radiation produced by the laser used in laser welding may affect surrounding electronic equipment and the human body. Radiation may not only interfere with the normal operation of surrounding electronic equipment but may also have a certain impact on the physiological functions of the human body, such as affecting cell structure and function
High-temperature hazards
During the laser welding process, the temperature of the welding point can reach thousands of degrees Celsius. Hot environments can cause burns to workers, especially if they are not handled properly or if appropriate protective measures are not taken. In addition, high temperatures can cause fire and explosion risks, posing potential threats to workplace safety.
Although laser welding plays an important role in modern industries, workers and employers must seriously treat many aspects of harm that laser welding may bring, and take effective prevention and protection measures environment.

How to take preventive measures?
To effectively prevent the possible harm caused by laser welding, a series of comprehensive measures must be taken to comprehensively prevent personal protection, working environment control, equipment safety management, and other aspects. The following are protective measures against various hazards caused by laser welding:
Personal protective measures
- Eye protection: Workers should wear laser protective glasses that meet relevant standards to effectively block the direct irradiation of laser beams to the eyes and reduce the risk of eye injury.
- Skin protection: Wear protective clothing, especially on hands and other exposed parts, and use appropriate protective gloves to reduce direct skin contact with smoke and possible harmful substances generated by laser welding.
- Respiratory system protection: Wear standard dust masks or respiratory protective equipment to prevent inhalation of harmful fumes produced by welding and reduce harm to the respiratory system.
- Noise prevention measures: In high-noise environments, workers should wear earplugs or earmuffs to effectively reduce noise damage to hearing organs and ensure the hearing health of workers.
Work environment control
- Ventilation facilities: Establish an effective ventilation system to eliminate harmful gases and smoke generated by laser welding promptly and keep the working environment clean.
- Isolation measures: Set up isolation facilities in the laser welding area to restrict the entry of non-essential personnel and reduce the impact of the laser beam on surrounding people.
- Temperature control: Take effective temperature control measures, such as providing adequate ventilation and cooling equipment in high-temperature working environments, to reduce the hazards of high temperatures to workers.
Device security
- Regular inspection and maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of laser welding equipment to ensure normal operation of the equipment and reduce the impact of equipment failure on the working environment.
- Radiation protection: Set up standard radiation protection facilities around laser welding equipment to effectively block the electromagnetic radiation generated by the laser generator and protect surrounding electronic equipment and the human body from the effects of radiation.
- Training and education: Provide necessary training and education for personnel engaged in laser welding to understand the potential hazards of laser welding, learn the correct use of personal protective equipment, and master the skills to respond to emergencies.
Management and monitoring
- Hazard source monitoring: Regularly monitor hazard sources in the laser welding working environment, including optical radiation, noise, gas, etc., to ensure that environmental safety meets standards.
- Health monitoring: Carry out health monitoring of workers, especially occupational health examinations related to laser welding, to detect and deal with potential health problems promptly.

The importance of preventing laser welding hazards
The importance of preventing laser welding hazards is not only related to the individual health and safety of employees but also involves the stability and sustainable development of the entire working environment. Here are a few key aspects to highlight this:
Maintain the health of employees
- Personal safety: Harmful substances such as optical radiation, smoke, and gases generated during the laser welding process pose a threat to the health of employees. Through effective preventive measures, the harm of laser welding to the eyes, skin, respiratory system, etc. can be reduced.
- Occupational disease prevention: Long-term exposure to harmful substances that may be produced during the laser welding process makes workers vulnerable to threats to the respiratory system, hearing organs, etc., which in turn leads to the occurrence of occupational diseases. Effective preventive measures can help reduce the risk of illness and improve the quality of professional life of employees.
Promote workwear efficiency and quality
- Avoid production disruptions: Laser welding hazards can lead to worker health issues or even accidents that can cause production disruptions. By preventing the occurrence of hazards, production continuity can be maintained and work efficiency improved.
- Reduce error rates: Light radiation and noise during the laser welding process may cause worker fatigue and inattention, thereby increasing the error rate in production. Effective preventive measures can help reduce worker fatigue during operations.
Environmental protection and social responsibility
- Reduce environmental pollution: Smoke, gas, and other harmful substances generated by laser welding are not only harmful to practitioners, but may also cause pollution to the surrounding environment. Through effective preventive measures, the emission of harmful substances can be reduced, the environmental burden can be reduced, and it is in line with corporate social responsibility.
- Social Image and Compliance: By actively taking preventive measures, companies can establish a good social image.
Technological innovation and sustainable development
- Promote technological development: Awareness of the hazards of laser welding prompts companies to conduct more research and development work and promote the improvement and innovation of laser welding technology to reduce its hazards.
- Improve enterprise competitiveness: By adopting the latest preventive measures, enterprises can improve the safety of the working environment, attract and retain excellent employees, and enhance the overall competitiveness of the enterprise.
Summarize
As an efficient and precise welding technology, laser welding has brought significant progress to the industrial field. However, we cannot ignore its potential hazards. Ensuring the health and safety of workers is not only a manifestation of corporate social responsibility but also the cornerstone of improving work efficiency and promoting sustainable development of the industry. By comprehensively understanding the hazards of laser welding and formulating scientific preventive measures, we can create a safer and healthier working environment while promoting technological progress.
Contact information
- Email:[email protected]
- Skype:[email protected]
- Wechat: +86-19963414011
Address to send the proofing materials
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
Related Blog