Product Introduction
Types of 4 Axis CNC Routers
-

AKM-4A1 CNC Router
Rated 4.50 out of 5$10,800.00 – $12,400.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

AKM-4A2 CNC Router
Rated 4.75 out of 5$14,000.00 – $15,600.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

AKM-4A3 CNC Router
Rated 4.50 out of 5$19,000.00 – $20,600.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
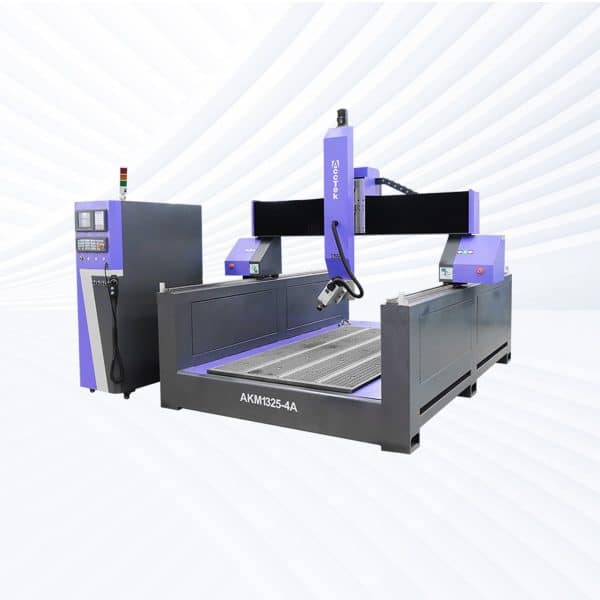

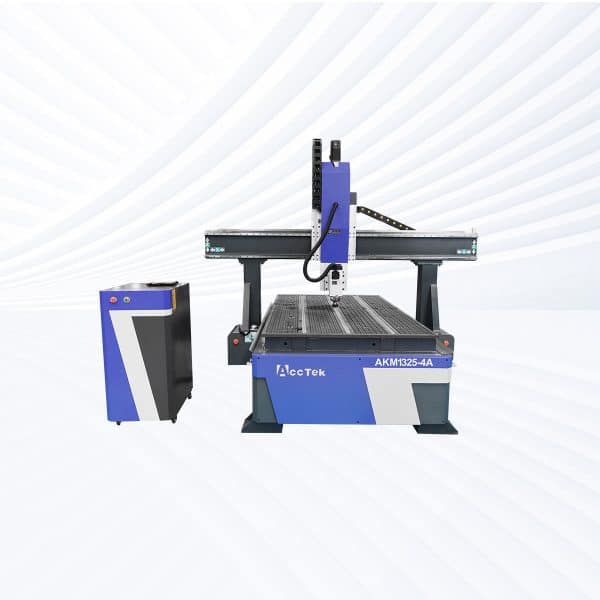
AKM1325-4A CNC Router
Rated 5.00 out of 5$10,800.00 – $19,000.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

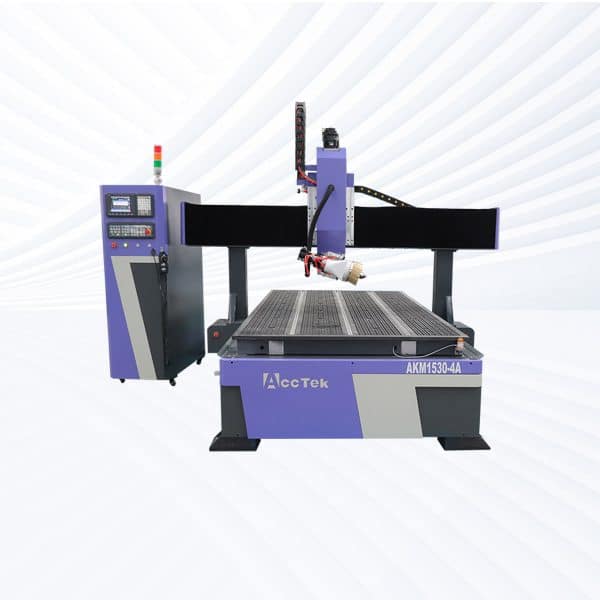
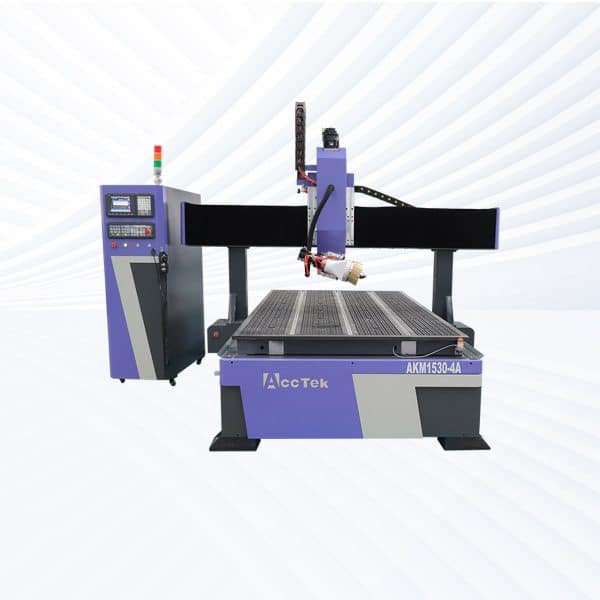
AKM1530-4A CNC Router
Rated 5.00 out of 5$11,400.00 – $19,600.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

AKM2030-4A CNC Router
Rated 5.00 out of 5$12,000.00 – $20,200.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

AKM2040-4A CNC Router
Rated 5.00 out of 5$12,400.00 – $20,600.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

AKM1325C-4A CNC Router
Rated 5.00 out of 5$14,000.00 – $19,000.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Application of 4 Axis CNC Routers







Customer Testimonials
4 Axis CNC Routers VS Other Engraving Machines
| Comparison Item | 4 Axis CNC Router | Laser Engraving Machine | CNC Milling Center | CNC Lathe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis Configuration | X, Y, Z + A (±180° spindle swing) | Typically X, Y (Z for focus) | X, Y, Z (3 to 5 axis options) | X, Z (rotating workpiece) |
| Spindle Movement | Tilts and rotates for angled cutting | Fixed focus head | Linear toolpath | Stationary tool, rotating part |
| Ideal For | Complex 3D carving, angled surfaces | Flat surface engraving | Precision 3D part machining | Cylindrical part shaping |
| Material Compatibility | Wood, plastic, foam, soft metals | Wood, acrylic, coated metals | Metals, plastics, and composites | Metals and plastics |
| Undercutting Capability | Yes (swinging spindle) | No | Yes (multi-axis only) | No |
| Part Repositioning Needed | No (multi-angle in one setup) | Yes (for multi-side marks) | Often required for angles | Yes |
| Machining Depth | Medium to deep | Shallow marking only | Deep with precision | Deep for round parts |
| Complexity of Shapes | High (3D and multi-angled) | Low to medium (2D/flat) | High (complex geometry) | Low (rotationally symmetrical) |
| Production Flexibility | High (sculpture, mold, furniture) | Medium (limited to surface marks) | High (prototypes, high tolerance) | Medium |
| Cutting Precision | High (±0.1 mm) | Very high (±0.01 mm) | Very high (±0.01 mm) | High (rotational parts) |
| Speed | Fast for soft materials | Very fast on thin materials | Moderate | Fast for round parts |
| Tool Wear | Moderate (depends on material) | None | High (especially for metals) | Medium |
| Automation Compatibility | High (CNC control) | High | High | High |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate | Low | High | Medium |
| Ideal Applications | Sculptures, mold making, 3D carving | Signage, tags, surface etching | Aerospace parts, molds, and tooling | Shafts, bushings, cylindrical items |
Why Choose Us
High Precision & Efficiency
AccTek CNC routers deliver fast, accurate results with minimal errors, supporting intricate designs and mass production across the woodworking, plastic, and metal industries.
Robust and Durable Design
Our machines are built with high-quality frames and components, ensuring long service life, high load-bearing capacity, and stability during high-speed operations.
Intelligent Control Systems
Equipped with user-friendly interfaces and smart controllers, our routers offer smooth motion control, automatic toolpath optimization, and easy integration with various CAD/CAM software.
Flexible Customization
From machine size to spindle power and motor type, we offer flexible configurations to suit different production needs, budgets, and material requirements.
Related Resources

What Is CNC Routing?
Discover the fundamentals of CNC routing, its applications, advantages, challenges, and how advanced CNC technology enhances precision and efficiency across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Can 4-Axis CNC Routers Do?
- Angled Surface Cutting: The oscillating spindle can tilt to cut bevels, chamfers, or angled edges without needing a special fixture. Useful in mold making, edge profiling, and decorative work.
- Deep 3D Carving: Tilting the tool allows for smoother surface finishing on complex 3D shapes by maintaining a better cutting angle, improving detail, and reducing tool marks.
- Improved Tool Contact: By tilting the spindle to match the part’s geometry, the machine can keep the tool in optimal contact, extending bit life and improving cut quality.
- Sloped Drilling or Routing: Drill or route holes and channels at an angle without repositioning the part—helpful in furniture making, cabinetry, and aerospace panels.
- More Efficient Multi-Axis Machining: While not as versatile as full 5-axis machines, a 4-axis CNC router with oscillating capability bridges the gap, allowing semi-complex geometries with fewer setups and more precision.
How To Choose 4-Axis CNC Routers?
- Understand Your Application:
- Angled drilling or routing
- Undercuts and compound curves
- 3D mold making and surface detailing
- Furniture, cabinetry, or aerospace panels with angled features
- If your work involves these, an oscillating 4-axis CNC is a smart choice.
- Spindle Power (Match to Material):
- 0kW–4.5kW: Sufficient for wood, plastics, MDF, and light composite jobs.
- 5kW–7.5kW: Better for hardwoods, heavy-duty machining, or deeper cuts at high speeds.
- Tilting the spindle adds mechanical stress, so power matters.
- Strong, Rigid Frame:
- Look for a steel or industrial aluminum frame—essential for accuracy during angled cuts.
- The machine must stay rigid even when the spindle tilts at extreme angles.
- Axis Travel and Z-Clearance:
- Confirm enough Z-axis clearance to allow for the spindle to tilt without hitting the workpiece or table.
- Larger parts or deep carvings need more vertical space.
- Controller and Software:
- Choose a controller that handles 4-axis simultaneous motion, like Syntec, RichAuto A11, or Mach4.
- Ensure compatibility with software that supports 4-axis toolpaths, such as Fusion 360, PowerMill, or ArtCAM.
- Toolpath and Simulation Capabilities:
- You’ll need an accurate 4-axis simulation to prevent tool crashes and verify motion before running a job.
- CAM software should allow you to define spindle angles per operation.
- Cooling and Dust Collection:
- Air- or water-cooled spindle to handle longer jobs with more complex motion.
- A flexible dust shoe that moves with the oscillating spindle helps maintain visibility and cleanliness.
- Service and Support:
- Look for vendors who offer tech support, spare parts, and training, especially for machines with advanced axis movement.
- Good support matters more with 4-axis CNC routers due to the added complexity.
How Much Do 4-Axis CNC Routers Cost?
- Standard 4-Axis CNC Router ($12,000–$15,000): These machines include a tilting spindle but no automatic tool changer. Ideal for workshops doing detailed woodwork, cabinetry, mold making, or angled drilling. They provide solid performance for medium-duty tasks where multiple tool changes aren’t needed frequently.
- ATC 4-Axis CNC Router ($15,000–$25,000): Includes an Automatic Tool Changer, allowing the spindle to switch tools mid-job without manual intervention. Great for high-efficiency workflows, production runs, or jobs requiring multiple tool types (e.g., roughing, finishing, engraving). This version is faster, more flexible, and suited for professional and industrial users.
What Materials Can 4-Axis CNC Routers Process?
- Wood
- Softwoods: Pine, cedar, fir
- Hardwoods: Oak, walnut, maple, cherry
- Engineered wood: Plywood, MDF, particle board
- Plastics
- Acrylic (PMMA)
- Polycarbonate
- PVC
- HDPE
- Foam
- Rigid foam
- Polyurethane foam
- EVA foam
- Composites
- Carbon fiber
- Fiberglass
- Phenolic
- Aluminum (Light-duty)
- Soft aluminum
- Cast aluminum plates
- Solid Surface Materials
- Corian
- Acrylic stone
- Similar synthetic surfaces
What Are The Disadvantages Of 4-Axis CNC Routers?
- Higher Cost: Machines with tilting spindles are more expensive than standard 3-axis CNC routers due to added mechanics, motors, and control systems. This includes both purchase price and maintenance costs.
- Increased Complexity: Programming angled toolpaths requires more advanced CAD/CAM software and greater operator experience. Mistakes in angle setup can lead to part errors or tool crashes.
- Larger Size and Heavier Build: To support spindle tilting, the machine frame often needs to be stronger and larger, which takes up more floor space and may require a reinforced foundation.
- Slower Machining Speed: Oscillating motion can reduce cutting speed, especially on complex contours. Tilting also increases toolpath length, which may extend cycle times.
- More Maintenance Points: The oscillating spindle assembly has more moving parts—bearings, motors, pivot mechanisms—that require regular maintenance and are more prone to wear.
- Limited Metal Cutting Capability: Even with spindle tilt, these machines are not built for hard metals like steel or titanium. They are best suited for wood, plastics, foam, and soft metals like aluminum.
- Software Compatibility Requirements: Not all CAM software supports 4-axis tilting motion natively. You may need to upgrade to more advanced (and more expensive) software to take full advantage of the machine.
What Spindle Power Options Are Available for 4-Axis CNC Routers?
- 6.0kW Spindle
- Ideal for medium-duty use in woodworking, plastics, and composites.
- Provides enough power for most 3D carving, angled drilling, and light aluminum cutting.
- Best for shops doing moderate production with occasional complex surface work.
- 7.5kW Spindle
- A strong choice for continuous use and more demanding materials like hardwoods, solid surface, and dense composites.
- Handles deeper cuts, faster feed rates, and longer tool life under heavier loads.
- Well-suited for industrial shops doing mold making, cabinetry, or high-volume 4-axis work.
- 9.0kW Spindle
- Heavy-duty spindle built for high-performance machining.
- Excellent for cutting large, complex parts with high spindle tilt usage.
- Recommended for shops dealing with large 3D parts, tight tolerances, or extended daily operation.
What Is The Lifespan Of 4-Axis CNC Routers?
- Typical Lifespan
- 8–15 years with proper maintenance and responsible use. High-end industrial models may last longer, especially if used in clean, controlled environments.
- Spindle Lifespan
- Air-cooled spindles: Usually last 6,000–10,000 hours
- Water-cooled spindles: Offer better heat management and may last longer with heavy or continuous tilt operations
- Spindles are wear parts and often need replacement during the machine’s lifetime.
- Oscillating Axis Wear
- The ±90° tilt mechanism introduces extra moving parts—gears, motors, and linkages—which can wear faster than the standard X, Y, and Z axes. Regular maintenance (like checking pivot alignment and lubrication) helps extend its service life.
- Factors That Affect Lifespan
- Usage intensity: Heavy daily use wears parts faster
- Materials processed: Harder materials = more wear
- Build quality: A rigid frame, precision rails, and industrial-grade components last longer
- Maintenance: Cleanliness, lubrication, and calibration make a big difference
- Environment: Dusty, hot, or humid workshops reduce component life
What Maintenance Is Required For 4-Axis CNC Routers?
- Daily Maintenance
- Clean the Work Area: Remove dust, chips, and debris from the table, rails, and moving parts.
- Inspect Tools and Bits: Check for wear, cracks, or dull edges. Replace or sharpen as needed.
- Lubricate Rails and Lead Screws (if not automatic): Apply manufacturer-approved lubricant to linear guides and ball screws to reduce wear.
- Check for Air Leaks (if pneumatic): Ensure all air lines are tight and pressure is stable if your system uses pneumatics.
- Weekly Maintenance
- Check Spindle Condition: Listen for unusual noise, check for heat buildup, and inspect for vibration.
- Inspect Oscillating Axis Components: Examine the tilt mechanism—gears, motors, bearings, and pivot points—for wear, misalignment, or loose hardware.
- Verify Axis Movement: Jog each axis (including the tilt axis) to ensure smooth, accurate travel without binding.
- Clean and Inspect Cable Tracks and Connectors: Remove debris and check for wear or fraying in drag chains and wiring.
- Monthly Maintenance
- Tighten Bolts and Fasteners: Vibration can loosen frame bolts, tilt motor mounts, and spindle brackets—tighten all structural components.
- Check and Adjust Belt or Gear Tension (if applicable): Some tilt axes use belt or gear drives that can loosen over time.
- Clean and Re-lubricate Oscillating Joints or Bearings: Apply grease or oil to pivot points and check for bearing wear.
- Run Calibration Test: Confirm machine accuracy with test cuts and adjust offsets or toolpaths if needed.
- Annual or Long-Term Maintenance
- Replace Worn Bearings or Spindle (as needed): Spindles and oscillating motors eventually wear out—replace when noise, vibration, or tolerance loss occurs.
- Inspect Control System and Update Software: Ensure firmware is up to date and settings are optimized for 4-axis motion.
- Full Mechanical Inspection: Evaluate the machine’s structural and motion components, especially the tilt mechanism, for long-term wear or misalignment.
