Product Introduction
Types of Fiber Laser Marking Machines
-
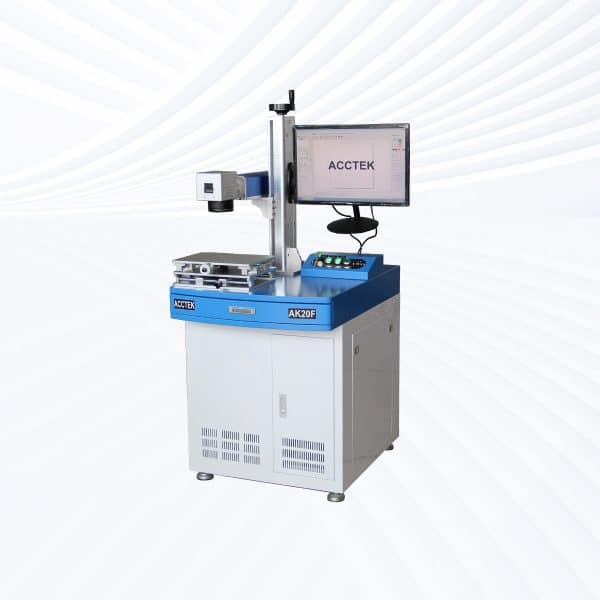

Desktop Fiber Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.50 out of 5$2,000.00 – $20,200.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

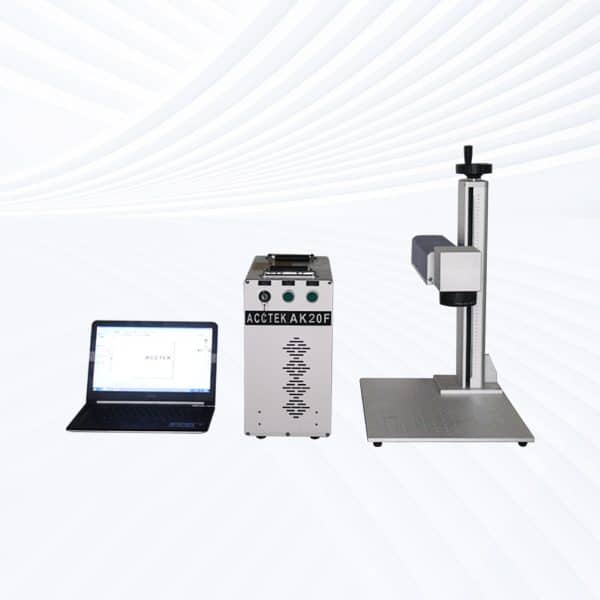
Handheld Fiber Laser Marking Machine
Rated 5.00 out of 5$2,150.00 – $20,350.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

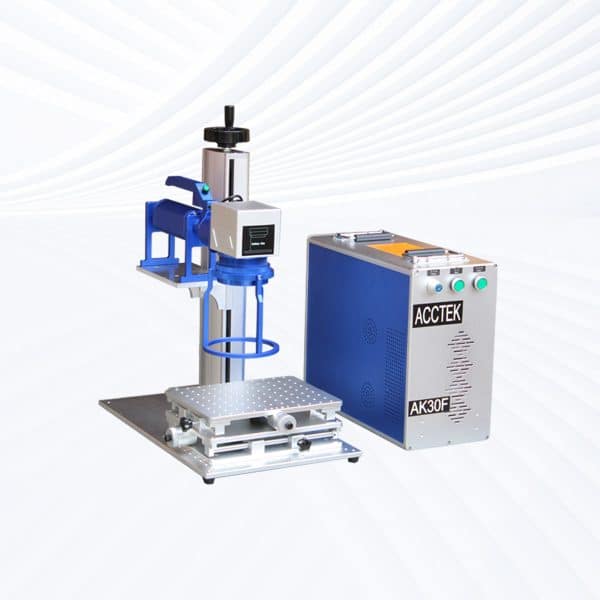
Split Fiber Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$2,000.00 – $20,200.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
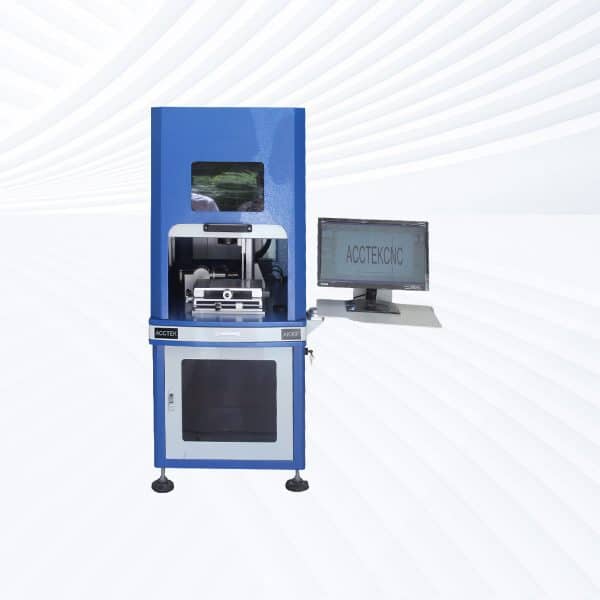

Enclosed Fiber Laser Marking Machine
Rated 5.00 out of 5$12,200.00 – $20,900.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
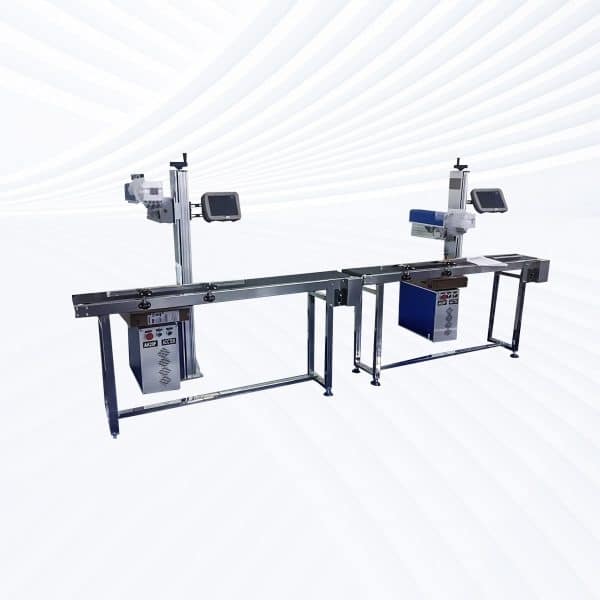

Flying Fiber Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$3,300.00 – $21,500.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
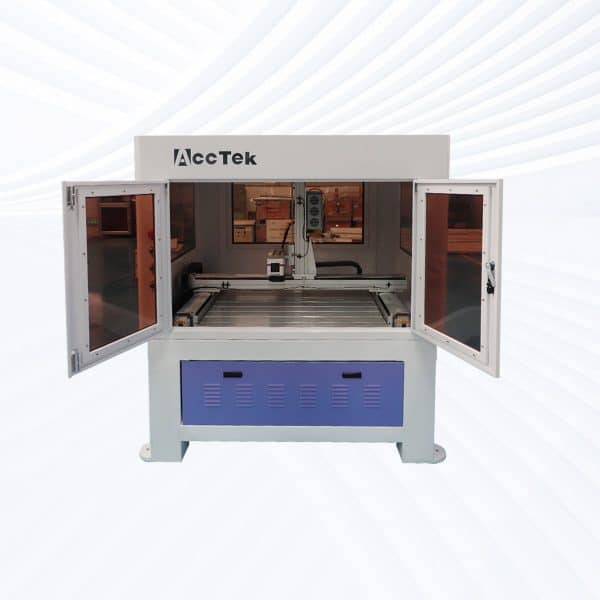

Screw Drive Fiber Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.75 out of 5$7,700.00 – $27,000.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
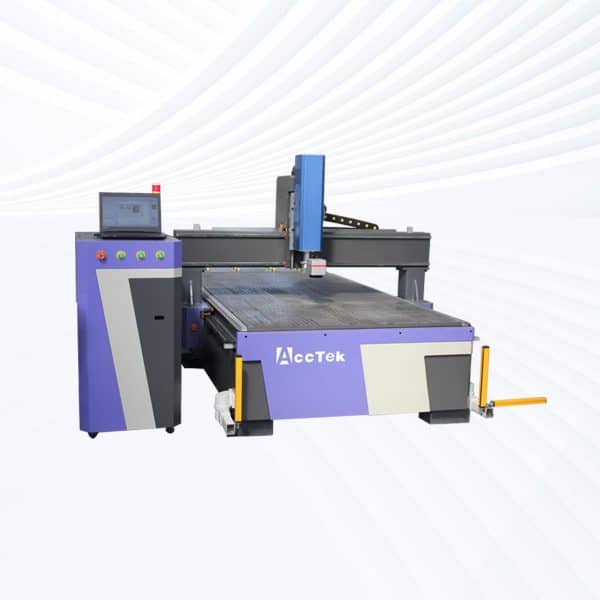

Rack Drive Fiber Laser Marking Machine
Rated 4.50 out of 5$7,800.00 – $26,800.00 This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Application of Fiber Laser Marking Machines







Customer Testimonials
Fiber Laser Marking Machine VS Other Marking Machines
| Comparison Item | Fiber Laser Marking | Dot Peen Marking | Inkjet Printing | Stamping | Chemical Etching |
| Marking Method | Focused laser beam (non-contact) | Mechanical impact pin (contact) | Ink droplets (non-contact) | Die pressure (contact) | Chemical reaction (contact) |
| Marking Precision | Very high (±0.01 mm) | Moderate | Low to moderate | Moderate | High |
| Marking Speed | Fast | Medium | Very fast | Moderate | Slow |
| Marking Durability | Permanent, fade-resistant | Permanent | Temporary, can fade | Permanent | Permanent |
| Surface Damage | None or minimal | Surface indentation | No damage | Surface deformation | Minor etching |
| Material Compatibility | Metals, some plastics | Metals only | Paper, plastic, coated surfaces | Metals only | Metals, some plastics |
| Graphic Flexibility | High (text, logos, codes, etc.) | Limited | Moderate | Limited | Moderate |
| Automation Capability | High, CNC compatible | Moderate | High | Low | Low |
| Consumables Required | No | Yes (pins) | Yes (ink) | Yes (dies) | Yes (chemicals, masks) |
| Maintenance Requirements | Low | Medium | High | Low | High |
| Operating Cost | Low after setup | Low | High ongoing cost | Low | High |
| Noise Level | Very low | High | Low | High | Low |
| Marking Depth Control | Yes, highly adjustable | Limited | No depth | Deep, fixed | Limited |
| Environmental Impact | Clean, no pollution | Low | High (VOC, ink waste) | Low | High (chemical waste) |
| Ideal Applications | Industrial metals, traceability, branding | Equipment IDs, tool marks | Expiry dates, packaging codes | Simple batch metal marking | Detailed permanent metal marks |
Why Choose Us
High Precision
Our machines deliver sharp, detailed markings with excellent contrast, suitable for complex patterns and small components across metal, plastic, and other materials.
Fast Processing
Designed for speed and efficiency, our systems complete marking tasks quickly without compromising quality, making them ideal for high-volume production environments.
Low Maintenance
With durable components and minimal consumables, our machines offer stable long-term performance, reducing downtime and keeping operating costs low.
Flexible Solutions
We provide a variety of models and customization options to suit different materials, marking needs, and production setups, ensuring the right fit for your business.
Related Resources

What Is Laser Marking?
Discover the fundamentals of laser marking, its types, applications, advantages, and key considerations. Learn how this advanced technology enhances precision, durability, and efficiency across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Fiber Laser Marking?
- Engraving: Removes material to create depth
- Etching: Melts the surface slightly to leave a shallow mark
- Annealing: Heats the surface to change color (no material removed)
What Laser Power Options Are Available For Fiber Laser Marking Machines?
- 20W
- Ideal for basic marking on metals and plastics
- Best for small parts, serial numbers, barcodes, and logos
- Suitable for low to medium production tasks
- 30W
- More power for faster marking and light engraving
- Handles more complex designs and larger batch jobs
- A common choice for general industrial marking
- 50W
- Allows for deeper engraving, faster processing, and marking on tougher materials
- Used in tools, aerospace, and automotive part marking
- 60W
- Offers a balance of speed and depth, ideal for engraving hardened metals
- Suitable for medium to high-volume production environments
- 70W
- More powerful option for heavy-duty marking, deeper etching, and high-contrast results
- Used in industrial and manufacturing operations
- 100W
- Designed for deep engraving, large surface marking, and high-speed production
- Ideal for high-volume or continuous-use applications
How Much Do Fiber Laser Marking Machines Cost?
- Entry-Level Machines ($2,500 – $6,000)
- Power: 20W to 30W
- Best for basic marking on metals and some plastics
- Good for small businesses, hobbyists, or low-volume jobs
- Compact design, manual focus, and limited automation
- Mid-Range Machines ($6,000 – $15,000)
- Power: 30W to 50W
- Offers faster marking, light engraving, and better reliability
- Ideal for moderate production environments
- May include rotary attachments and better software
- High-End Machines ($15,000 – $30,000)
- Power: 60W to 100W
- Built for deep engraving, large-scale marking, and continuous use
- Often equipped with auto-focus, high-end lenses, MOPA technology, and industrial cooling
- Designed for industrial, automotive, aerospace, or electronics production
What Materials Can Be Marked With Fiber Lasers?
- Metals (Excellent Performance)
- Stainless steel
- Aluminum (including anodized)
- Brass
- Copper
- Titanium
- Carbon steel
- Tool steel
- Precious metals (gold, silver, platinum)
- Plastics (Selective Performance)
- ABS
- Polycarbonate
- PVC
- PET
- PEEK
- PA (Nylon)
- Coated and Treated Surfaces
- Anodized aluminum
- Painted or powder-coated metals
- Plated surfaces (chrome, nickel)
- Other
- Some ceramics
- Certain composites
What File Formats Do Fiber Laser Marking Machines support?
- Vector Formats
- DXF (.dxf): From CAD software (AutoCAD, SolidWorks)
- AI (.ai): Adobe Illustrator files
- SVG (.svg): Scalable vector graphics
- PLT (.plt): Plotter files, commonly used in engraving
- PDF (.pdf): If saved with vector data
- Image Formats
- BMP (.bmp): Preferred for logos and grayscale engraving
- JPG/JPEG (.jpg): Common photo format
- PNG (.png): Supports transparency; good for clean logos
- GIF (.gif): Occasionally supported for simple graphics
- Text and Data Files
- TXT (.txt): Used for importing serial numbers, codes, batch info
- CSV (.csv): For bulk marking with variable data
- G-code (.nc, .tap, .gcode): In some advanced systems
How Large Marking Areas Do Fiber Laser Marking Machines Support?
- 110×110 mm
- This is the standard size for many fiber laser machines.
- Ideal for small to medium parts, such as tools, tags, nameplates, and electronic components.
- Offers high precision and detail, making it great for barcodes, serial numbers, and fine logos.
- 200×200 mm
- A larger marking area for bigger parts or multiple pieces in one batch.
- Useful in industrial production, metal sheets, or when marking multiple items without repositioning.
- Slightly lower marking resolution compared to smaller lenses, but still precise for most tasks.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Fiber Laser Marking Machines?
- Not Ideal for Non-Metals: Fiber lasers perform best on metals and some plastics, but they are not suitable for organic materials like wood, glass, acrylic, paper, or leather. For those, CO2 or UV lasers are better options.
- Higher Initial Cost: While cost-effective long-term, fiber laser machines have a higher upfront price compared to CO2 machines at similar power levels, especially for higher-wattage systems.
- Limited Color Marking: Standard fiber lasers can’t produce color effects. Only MOPA fiber lasers can do color marking on stainless steel, and even then, it’s limited to specific conditions and materials.
- Larger Marking Areas Reduce Detail: To mark larger areas, wider lenses are used—but this can lead to lower resolution and beam quality at the edges of the marking field.
- Safety Concerns: Fiber lasers are Class 4 lasers and can be hazardous if not properly enclosed. Users need to follow strict safety protocols, including protective eyewear and shields.
- Challenging on Transparent Materials: Because the 1064 nm wavelength passes through transparent and reflective non-metal surfaces, materials like glass or clear plastic are hard to mark without special coatings or pre-treatment.
What Are The Operating Environment Requirements For Fiber Laser Marking Machines?
- Temperature Range
- Ideal: 15℃ to 30℃ (59℉ to 86℉)
- Avoid extremes—too hot or too cold can affect laser stability and electronics.
- Use air conditioning in hot climates for consistent temperature control.
- Humidity
- Recommended: 30% to 70% relative humidity, non-condensing
- High humidity can cause condensation, rust, or short circuits.
- Use dehumidifiers in humid environments if needed.
- Dust-Free, Clean Area
- Keep the workspace clean and dust-free to protect optical components and fans.
- Install in a well-ventilated area, but away from open-air contaminants like sawdust or chemical fumes.
- Stable Power Supply
- Use 220V (or as specified by the machine) with surge protection or a voltage stabilizer.
- Unstable power can lead to errors or damage to the laser source or controller.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction
- Proper fume extraction or air filtration is required to remove smoke, odors, and particles from marked materials.
- Especially important when marking plastics, coated metals, or synthetic materials.
- Vibration-Free Surface
- Place the machine on a flat, stable, vibration-free table or floor.
- Vibration can affect marking precision and may damage components over time.
